Welcome, curious minds, to a truly extraordinary journey into the depths of science and biology. In today’s YouTube video, titled “Unveiling the Secret: The Art of Urine Creation,” we dive headfirst into the complex process behind urine formation. Yes, you heard it right, urine – the often overlooked but absolutely vital liquid our bodies produce to rid us of waste and maintain our internal balance.
So, my fearless adventurers, let us embark on this enlightening expedition together. Imagine, if you will, the kidneys – dynamic and shape-shifting organs, tirelessly working to filter our blood. They are the unsung heroes responsible for removing waste substances, regulating water and electrolytes, and ultimately producing the enigmatic substance we know as urine.
To understand this artistic creation, we must explore the stages of urine formation: glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, and tubular secretion. Within the kidney’s functional unit, the nephron, lies the initiation of this intricate process – the glomerulus. Think of it as a network of capillaries, engaging in the first step of blood filtration.
Picture, if you can, a thin double-walled capsule surrounding this glomerulus, aptly named Bowman’s capsule. The space inside this capsule and around the glomerulus itself is known as Bowman’s space. As the blood traverses through the capillaries of the glomerulus, a phenomenon occurs – filtration. It causes select plasma contents to spill out into Bowman’s space through a magnificent filtration membrane, comprising three layers of capillary genius – valve endothelium, basement membrane, and epithelial podocytes.
Yet, dear companions, restrain your excitement, for not all particles of blood may pass through this extraordinary membrane. What passes into Bowman’s space, forming the filtrate, is a fluid of great importance – the primary urine.
Now, as we conclude our prelude to this captivating exploration, I urge you to ready yourselves for the wonders that lie ahead. Together, we shall unlock the secrets of urine creation, delving deeper into the complex workings of our dearly cherished bodies. Brace yourselves, my fellow seekers, for the art of urine creation awaits us just beyond the horizon, ready to amaze and educate us in the most extraordinary of ways.
– The Kidney’s Role in Urine Formation: A Detailed Look at Glomerular Filtration and Regulation
The kidney’s role in urine formation is a complex and intricate process that involves various steps and components. One of the key processes in urine formation is glomerular filtration, which takes place in the kidneys’ filtering units called nephrons. The glomerulus, consisting of a network of capillaries, acts as the primary site for filtering the blood.
At the beginning of the nephron, the glomerulus is enclosed by a thin, double-walled structure called Bowman’s capsule. The space inside the capsule, known as Bowman’s space, surrounds the glomerulus. As the blood travels through the capillaries of the glomerulus, a process of filtration occurs, causing certain plasma contents to spill out into Bowman’s space. This filtration process is facilitated by the glomerular filtration membrane, which consists of three layers – the endothelium, basement membrane, and podocytes.
The glomerular filtration membrane selectively allows some particles of blood to pass through while retaining others. The fluid that is filtrated from the capillary blood into Bowman’s space is called filtrate, and it forms the primary urine. This filtrate contains waste substances, excess water, and excess electrolytes, which are further processed and modified as urine travels through the rest of the nephron. The regulation of glomerular filtration and urine formation is crucial in maintaining the balance of water and electrolytes within the body fluids.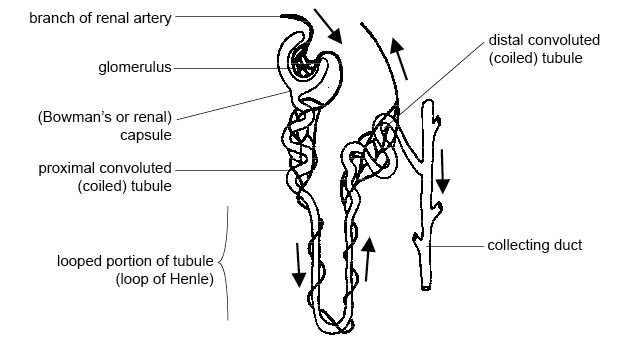
– Unraveling the Nephron: Understanding the Function of the Glomerulus and Bowman’s Capsule
The glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule play a crucial role in the filtration process of the kidneys. The glomerulus, a network tuft of capillaries, is the first step in filtering the blood. It filters waste substances from the blood and regulates water and electrolyte concentrations within the body fluids. This filtration process leads to the formation of urine, which is excreted outside the body through the urethra, carrying waste materials, excess water, and excess electrolytes.
At the beginning of the nephron, the glomerulus is surrounded by thin double-walled capsules called Bowman’s capsule. The space inside the capsule and surrounding the glomerulus is known as Bowman’s space. As the blood travels through the glomerular capillaries, filtration occurs, causing plasma contents to spill out into Bowman’s space through the glomerular filtration membrane. This membrane consists of three layers: the valve endothelium, basement membrane, and epithelial podocytes. While this membrane allows some particles of blood to pass through, not all fluids are filtered. The fluid that passes from the capillary blood into Bowman’s space is called filtrate and forms the primary urine.
Understanding the function of the glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule is crucial in comprehending the intricate process of urine formation. These structures serve as filters within the kidneys, removing waste substances and regulating the body’s water and electrolyte concentrations. By unraveling the mechanisms at play within the nephron, we gain insight into the remarkable processes that enable our body to maintain homeostasis and eliminate waste efficiently.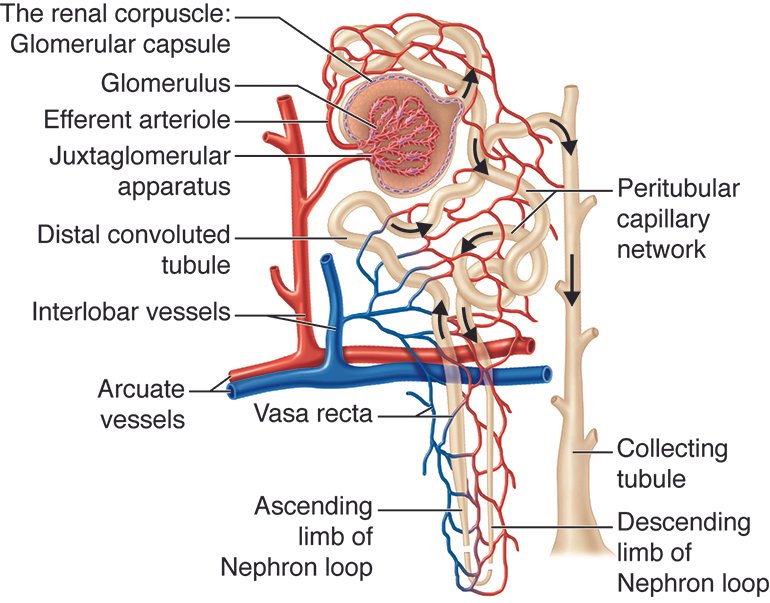
– Decoding the Glomerular Filtration Membrane: Its Structure and Role in Urine Formation
The glomerular filtration membrane is a crucial component of the kidney’s filtration process, playing a significant role in urine formation. This intricate structure is made up of three layers: the valve endothelium, basement membrane, and epithelial podocytes. Together, these layers form a semipermeable barrier that allows certain substances to pass through, while retaining others within the capillaries.
At the start of the nephron, the glomerulus, a network tuft of capillaries, acts as the primary filtration site. Surrounding the glomerulus is Bowman’s capsule, a double-walled capsule that collects the filtrate. The space inside the capsule, known as Bowman’s space, serves as the initial collection point for the filtrate.
As blood flows through the capillaries of the glomerulus, the glomerular filtration membrane selectively permits the passage of plasma contents into Bowman’s space. This filtration process is not indiscriminate, as the membrane strictly controls which substances can enter the filtrate. While some particles are allowed to pass through, others are held back, ensuring that vital components remain in the bloodstream.
The fluid that is filtrated from the capillary blood and collected in Bowman’s space is known as the filtrate, marking the formation of the primary urine. This filtrate contains waste substances, excess water, and electrolytes that have been removed from the blood. Ultimately, the primary urine undergoes further processing through tubular reabsorption and tubular secretion, leading to the consolidation of waste materials and the concentration of urine.
Understanding the structure and function of the glomerular filtration membrane is vital in comprehending how the kidneys perform their crucial task of waste elimination and maintaining electrolyte balance. By deciphering the intricate processes involved in urine formation, we can gain insights into the remarkable efficiency and precision of the renal system.
– From Filtrate to Primary Urine: Exploring the Journey of Waste Removal in the Kidneys
The kidneys play a vital role in removing waste substances from the blood and maintaining water and electrolyte concentrations in the body fluids. This waste removal process ultimately leads to the production of urine, which is then excreted from the body.
The journey of waste removal in the kidneys begins with glomerular filtration. The glomerulus, a network tuft of capillaries, acts as the first filter, removing waste substances from the blood. Surrounding the glomerulus is Bowman’s capsule, which is a thin, double-walled capsule. Inside this capsule is a space known as Bowman’s space.
As the blood passes through the capillaries of the glomerulus, filtration occurs, causing plasma contents to spill into Bowman’s space through the glomerular filtration membrane. This membrane consists of three layers: the valve endothelium, basement membrane, and epithelial podocytes. While this membrane allows some particles of blood to pass through, not all fluid is filtered. The fluid that is filtered from the capillary blood into Bowman’s space is referred to as filtrate, which then forms the primary urine.
Overall, this intricate process of glomerular filtration in the kidneys ensures the removal of waste substances from the blood, leading to the production of urine. It is through this journey that the kidneys play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of fluids and electrolytes in our bodies.
The Way Forward
In conclusion, the YouTube video “Unveiling the Secret: The Art of Urine Creation” sheds light on the fascinating process of urine formation in our bodies. We have learned that urine is the end product of the kidneys’ filtration process, where waste substances, excess water, and excess electrolytes are removed from the blood.
The kidneys play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of water and electrolyte concentrations in our body fluids. This intricate process involves glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, and tubular secretion. At the beginning of the nephron, the functional unit of the kidneys, the glomerulus acts as a network tuft of capillaries that filters the blood.
Bowman’s capsule, a thin double-walled structure, surrounds the glomerulus, creating Bowman’s space. The glomerular filtration membrane, consisting of three layers of capillary endothelium, basement membrane, and epithelial podocytes, allows some particles of blood to pass through while retaining others. The fluid that filtrates from the capillary blood into Bowman’s space is known as filtrate, forming the primary urine.
Understanding the art of urine creation helps us appreciate the intricacies of the human body’s regulatory systems. This video has provided valuable insights into the physiological processes occurring within our kidneys. By shedding light on the role of glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, and tubular secretion, we gain a deeper understanding of how our bodies maintain homeostasis.
So next time you visit the restroom to dispose of your urine, remember the remarkable journey it took to be formed. The art of urine creation is truly a marvel, quietly working behind the scenes to maintain our overall health and well-being.