Know about bilateral knee osteoarthritis, and is it serious?
Osteoarthritis is a common degenerative joint disease that can affect various joints in the body, and one such area is the knees. When osteoarthritis affects both knees simultaneously, it is known as bilateral knee osteoarthritis. This condition can cause significant discomfort and impair mobility. In this article, we will explore the symptoms, causes, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment options, management techniques, prevention methods, as well as outlook and complications associated with bilateral knee osteoarthritis.
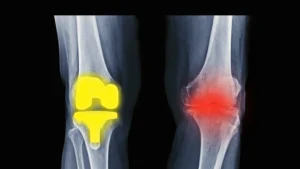
Symptoms
Individuals with bilateral knee osteoarthritis often experience symptoms such as:
-
- Joint pain:
The most common symptom of bilateral knee osteoarthritis is pain in both knees. This pain can be mild or severe and may worsen with activities like walking, climbing stairs, or standing for prolonged periods.
-
- Stiffness:
Stiffness in the knees, especially after periods of inactivity, is a common symptom of bilateral knee osteoarthritis. This stiffness usually improves with movement but may persist for an extended period.
-
- Swelling and inflammation:
Some individuals with bilateral knee osteoarthritis may experience swelling and inflammation in the affected knees. The joints may feel warm to the touch and appear red or swollen.
Causes
The exact cause of bilateral knee osteoarthritis is not yet fully understood. However, it is generally believed to be a combination of several factors, including:
-
- Age:
Advancing age is a significant risk factor for bilateral knee osteoarthritis. As one grows older, cartilage, the protective tissue that cushions the joints, begins to deteriorate naturally, leading to arthritis.
-
- Previous knee injuries:
Injuries to the knee joint, such as ligament tears or fractures, increase the risk of developing bilateral knee osteoarthritis. These injuries disrupt the joint’s normal structure, leading to accelerated degeneration.
-
- Obesity:
Excess weight places additional stress on the knee joints, accelerating the breakdown of cartilage and worsening bilateral knee osteoarthritis. Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the risk and severity of the condition.
Risk factors
Several factors increase the risk of developing bilateral knee osteoarthritis:
-
- Gender:
Women are more likely to develop bilateral knee osteoarthritis compared to men. This gender difference may be due to hormonal factors or differences in anatomical structure.
-
- Genetics:
Family history of knee osteoarthritis increases the likelihood of developing the condition. Certain genetic variations make individuals more susceptible to joint degeneration.
-
- Occupational factors:
Jobs that involve repetitive knee movements or heavy load-bearing activities can contribute to the development of bilateral knee osteoarthritis. Workers in occupations such as construction or manual labor are at a higher risk.
Diagnosis
Bilateral knee osteoarthritis is typically diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests. The doctor may:
-
- Record symptoms:
The doctor will ask about symptoms, their severity, and duration, as well as any triggering factors.
-
- Conduct a physical examination:
The affected knees will be examined for signs of swelling, tenderness, warmth, and limited range of motion. The doctor may also assess the patient’s gait and overall joint stability.
-
- Order imaging tests:
X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of the knees can help visualize the extent of joint damage and rule out other possible causes of knee pain.
Treatment
There is currently no cure for bilateral knee osteoarthritis, but various treatment options aim to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Common treatments include:
-
- Medications:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), analgesics, and corticosteroid injections can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation in the knee joints.
-
- Physical therapy:
A well-designed exercise program prescribed by a physical therapist can strengthen the muscles around the knees, improve joint mobility, and relieve pain. Modalities such as heat or ice applications may also be used.
-
- Surgical intervention:
In severe cases where conservative measures fail, surgical options like knee arthroscopy or knee replacement may be considered to relieve pain and restore function.
Management
In addition to medical treatments, individuals with bilateral knee osteoarthritis can manage their condition through:
-
- Weight management:
Losing excess weight can significantly reduce the stress on the knee joints, thereby alleviating symptoms and slowing down the progression of bilateral knee osteoarthritis.
-
- Assistive devices:
Using walking aids, such as canes or crutches, can provide support and reduce the load on the knees, making mobility easier for those with bilateral knee osteoarthritis.
-
- Pain management techniques:
Applying heat or cold packs to the knees, practicing relaxation techniques, or using over-the-counter topical creams can help manage pain and improve joint function.
Prevention
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent bilateral knee osteoarthritis, certain lifestyle modifications can reduce the risk:
-
- Maintain a healthy weight:
Avoiding obesity or overweight status can significantly decrease the strain on the knee joints and slow down the progression of bilateral knee osteoarthritis.
-
- Exercise regularly:
Engaging in low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, can strengthen the muscles around the knees, improve joint stability, and maintain flexibility.
-
- Protect the knees during physical activities:
Wearing appropriate protective gear, such as knee pads or braces, can reduce the risk of knee injuries that may lead to bilateral knee osteoarthritis.
Outlook and complications
Bilateral knee osteoarthritis is a chronic condition that can cause significant pain and stiffness. Without proper management, the symptoms may progressively worsen, leading to joint deformity and disability. It can impact an individual’s ability to perform daily activities, such as climbing stairs or walking long distances. However, with a combination of medical interventions, lifestyle modifications, and self-management strategies, the symptoms can be effectively controlled, improving overall quality of life for those with bilateral knee osteoarthritis.
Summary
Bilateral knee osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint condition that affects both knees at the same time. It is characterized by symptoms like joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. The causes of this condition are multifactorial, with age, previous knee injuries, and obesity being significant risk factors. Diagnosis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests. While there is no cure, various treatment options, including medication, physical therapy, and surgery, can help manage symptoms. Additionally, lifestyle modifications, such as weight management and regular exercise, can prevent its onset or slow down its progression. With proper management, individuals can effectively control the symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Sources:
1. Mayo Clinic. (2021). Osteoarthritis. www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/osteoarthritis/symptoms-causes/syc-20351925.
2. Arthritis Foundation. (2021). Arthritis Diet.