Compound Fractures: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Recovery
Introduction: Compound fractures, also known as open fractures, are severe injuries that occur when a broken bone pierces through the skin. This type of fracture requires immediate medical attention due to the potential for infection and other complications. In this article, we will explore the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and recovery of compound fractures.
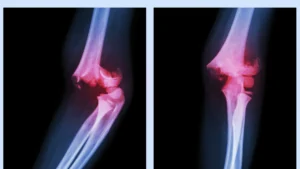
Overview
Compound fractures are classified as an orthopedic emergency. They are considered more severe than closed fractures because the broken bone exposes the surrounding tissues to the external environment. This exposure increases the risk of infection, which can have serious consequences if not treated promptly. Compound fractures often result from high-impact trauma, such as car accidents, falls from heights, or sports injuries. The severity of the fracture depends on various factors, including the location, extent of bone displacement, and the presence of additional injuries.
Symptoms and Causes
In addition to the obvious visible signs of a broken bone protruding through the skin, other symptoms of a compound fracture may include severe pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty moving the affected limb. The most common causes of compound fractures are high-velocity accidents, such as motorcycle crashes or industrial accidents, as well as sports injuries. The force applied to the bone is usually so strong that it surpasses the bone’s ability to withstand it, leading to the bone breaking and tearing through the skin.
Diagnosis and Tests
Diagnosing a compound fracture typically involves a thorough physical examination, medical history review, and imaging tests. The doctor will assess the injury site for any visible signs, such as bone protrusion or an open wound. X-rays are commonly used to determine the type and severity of the fracture, as well as to identify any associated injuries. In cases where a more detailed view is required, computed tomography (CT) scans may be necessary. These tests help doctors accurately evaluate the damage and plan an appropriate treatment course.
Management and Treatment
Immediate first aid for compound fractures involves stabilizing the injured limb and covering the wound to prevent infection. The primary goal of treatment is to clean the wound thoroughly, reduce the risk of infection, and promote healing. Depending on the severity of the fracture, treatment may include realigning the bone fragments through a surgical procedure called reduction. This is often followed by fixation, where screws, plates, or rods are used to keep the bone fragments in place. In some cases, a temporary external fixator may be utilized to secure the bone and allow for swelling to subside before surgery.
Prevention
Although accidents happen unpredictably, there are some measures that individuals can take to reduce the risk of compound fractures. These include wearing appropriate protective gear when engaging in high-risk activities, such as helmets for cyclists or knee pads for skateboarders. Maintaining good bone health through regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, and avoiding lifestyle factors that weaken bones, like smoking or excessive alcohol consumption, can also play a role in fracture prevention.
Outlook / Prognosis
The outlook for compound fractures varies depending on several factors, such as the individual’s overall health, the severity of the fracture, and timely treatment. With prompt medical attention and appropriate treatment, many compound fractures can heal successfully. However, complications such as infection, nerve or blood vessel damage, or poor wound healing may prolong the recovery process. Physical therapy, rehabilitation exercises, and ongoing medical monitoring are often necessary to regain full function and mobility of the affected limb. The overall prognosis for patients with compound fractures is generally good, but the recovery time can vary from weeks to months.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can compound fractures be treated without surgery?
A: In some cases, if the fracture is not severe and there is no risk of infection or complications, non-surgical treatment may be chosen. This often involves immobilizing the limb with a cast or splint to allow the bone to heal naturally.
Q: How long does it take to recover from a compound fracture?
A: Recovery time for compound fractures can vary depending on the individual and the specific fracture. On average, it may take several weeks to months for the bone to heal, and additional time for rehabilitation and regaining full function.
Q: Can compound fractures lead to long-term complications?
A: While most compound fractures heal successfully with proper treatment, there is a risk of long-term complications. These can include infection, delayed union or nonunion of the bone, persistent pain, nerve damage, or joint stiffness. Close medical monitoring and adherence to the prescribed treatment plan can help minimize these risks.
Conclusion: Compound fractures are severe injuries that require urgent medical attention. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment play a crucial role in achieving a successful recovery. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and management of compound fractures, individuals can take steps to prevent such injuries and promote bone health.