Welcome to the wonderful world of urine and the intricate process of glomerular filtration! In this blog post, we will delve into the mysteries of the kidneys, those remarkable organs responsible for filtering blood and maintaining the delicate balance of water and electrolytes within our bodies. But fear not, this isn’t just a science lesson in disguise – we’re here to demystify the art behind the formation of urine.
Imagine your kidneys as expert artists, meticulously working to remove waste substances from your blood and create a masterpiece known as urine. This masterpiece is then excreted from the body through the urethra, taking with it the excess water and electrolytes that we no longer need.
To understand the process of urine formation, we need to explore the fascinating world of the nephron – the functional unit of the kidneys. At the start of the nephron lies the glomerulus, a network of capillaries that plays a crucial role in the first step of filtering the blood. Surrounding the glomerulus is a thin double-walled capsule called Bowman’s capsule, creating a space known as Bowman’s space. As the blood travels through the capillaries of the glomerulus, the glomerular filtration membrane comes into play.
This remarkable membrane consists of three layers - the valve endothelium, basement membrane, and epithelial podocytes. It acts as a selective barrier, allowing some particles to pass through while retaining others. As a result, a portion of the capillary blood is filtrated into Bowman’s space, forming what we call filtrate – the primary urine.
So, join us as we unravel the mysteries of glomerular filtration and explore the intricacies of urine formation. Brace yourself for a fascinating journey through the inner workings of the kidneys, where science and art converge to create the remarkable process that is demystifying glomerular filtration.
Heading 1: The Function of Glomerular Filtration in Kidneys
Glomerular filtration in the kidneys is a crucial function that the organs perform. It serves as a filtration system that removes waste substances from the blood and regulates water and electrolyte concentrations within the body fluids. The end result of this process is the production of urine, which is excreted outside of the body through the urethra. The urine consists of waste materials, excess water, and excess electrolytes.
The formation of urine involves several steps, including glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, and tubular secretion. At the beginning of the nephron, the functional unit of the kidneys, lies the glomerulus. The glomerulus is a network tuft of capillaries that plays a significant role in filtering the blood. It is encased in thin double-walled capsules called Bowman’s capsule. The space inside the capsule and surrounding the glomerulus is known as Bowman’s space.
During the process of glomerular filtration, as the blood travels through the capillaries of the glomerulus, many plasma components are filtered out into Bowman’s space through the glomerular filtration membrane. This membrane consists of three layers: the capillary valve endothelium, the basement membrane, and the epithelial podocytes. While this membrane allows some particles of blood to pass through, it retains others. The fluid that is filtered from the capillary blood into Bowman’s space is referred to as filtrate and forms the primary urine.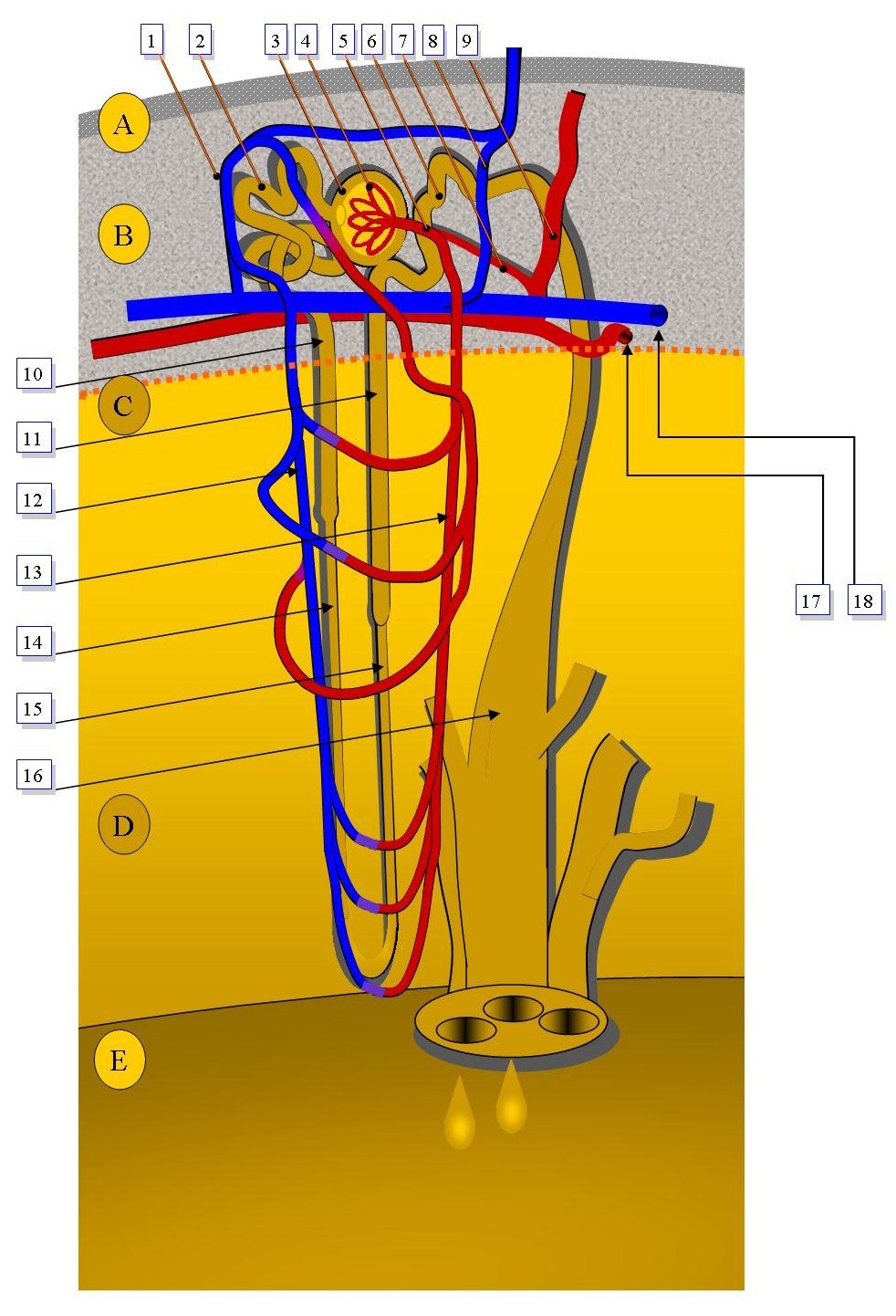
Heading 2: Understanding the Nephron and the Glomerulus
The nephron and the glomerulus are integral parts of the kidney’s filtration system. At the beginning of the nephron, the glomerulus, a network of tufted capillaries, performs the first step of filtering the blood. This vital process, known as glomerular filtration, removes waste substances from the blood and maintains water and electrolyte concentrations in the body fluids.
To facilitate glomerular filtration, the glomerulus is surrounded by thin double-walled capsules called Bowman’s capsules. Inside these capsules is Bowman’s space, which encompasses the glomerulus. As blood flows through the glomerular capillaries, the filtration process causes plasma contents to spill out into Bowman’s space, creating the filtrate. This filtration process occurs through the glomerular filtration membrane, which consists of three layers: the valve endothelium, basement membrane, and epithelial podocytes.
While the glomerular filtration membrane allows some particles of blood to pass through, it doesn’t permit all fluids to do so. The fluid that filters from the capillary blood into Bowman’s space is called filtrate and forms the primary urine. Understanding the nephron and the glomerulus is essential for comprehending the kidney’s intricate filtration process and the formation of urine.
Heading 3: Deconstructing the Glomerular Filtration Membrane
The glomerular filtration membrane is a vital component in the process of urine formation within the kidneys. This membrane consists of three layers of capillary: the valve endothelium, the basement membrane, and the epithelial podocytes. It is through this membrane that the blood is filtered, allowing some particles to pass through while preventing others from entering.
As the blood travels through the capillaries of the glomerulus, the filtration process occurs, causing plasma contents to spill out into a space called Bowman’s space. This space is surrounded by a thin double-walled capsule called Bowman’s capsule. The filtrate, which is the fluid that is derived from the capillary blood and enters Bowman’s space, is what forms the primary urine.
The glomerular filtration membrane functions as a selective barrier, ensuring that waste substances are removed from the blood while maintaining the optimal balance of water and electrolytes within the body fluids. This crucial process plays a significant role in maintaining overall bodily homeostasis. By understanding the intricate workings of the glomerular filtration membrane, we can gain insight into the sophisticated mechanisms that contribute to the production of urine and the regulation of bodily functions.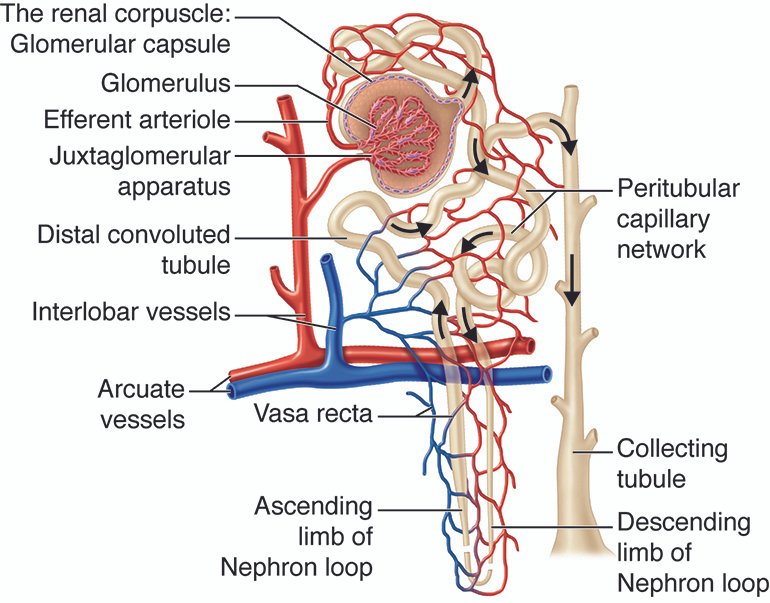
Heading 4: Maximizing Urine Formation and the Elimination of Waste
Urine formation is a complex process that involves various steps to maximize the production of urine and eliminate waste from the body. The kidneys, which are shaped organs, play a crucial role in this process as they filter the blood, removing waste substances and regulating water and electrolyte concentrations within the body fluids.
One of the key steps in urine formation is glomerular filtration, which occurs in the nephron, the functional unit of the kidneys. The glomerulus, a network of tufted capillaries, acts as a filter to separate the blood from waste products. Surrounding the glomerulus is Bowman’s capsule, which forms a double-walled capsule. Inside this capsule is the space known as Bowman’s space.
As the blood travels through the capillaries of the glomerulus, the filtration process causes plasma contents to spill out into Bowman’s space through the glomerular filtration membrane. This membrane consists of three layers: the valve endothelium, basement membrane, and epithelial podocytes. While some particles of blood are allowed to pass through this membrane, not all fluid from the capillary blood enters Bowman’s space. The fluid that does make its way into Bowman’s space is called filtrate and forms the primary urine.
Aside from glomerular filtration, other steps involved in urine formation are tubular reabsorption and tubular secretion. These processes further refine the filtrate by reabsorbing essential substances back into the bloodstream and secreting additional waste products into the urine. Through this intricate process, the kidneys maximize urine formation, ensuring the elimination of waste substances, excess water, and excess electrolytes from the body through the urethra.
In Retrospect
In the intriguing world of glomerular filtration, we have uncovered the fascinating process by which our kidneys filter blood, eliminating waste substances and maintaining the delicate balance of water and electrolytes within our bodies. As we delved into this topic, we witnessed the birth of urine – the end product of this intricate filtration dance.
Urine formation, as we discovered, involves various steps such as glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, and tubular secretion. At the heart of this process lies the nephron, the functional unit of the kidneys. Here, we met the glomerulus – a network of capillaries diligently filtering the blood. This remarkable structure is guarded by the Bowman’s capsule, a thin double-walled capsule whose inner space, known as Bowman’s space, cradles the glomerulus.
As the blood traverses the capillaries of the glomerulus, an elaborate performance unfolds. Filtration occurs, causing plasma contents to overflow into Bowman’s space through the glomerular filtration membrane. This membrane, composed of three layers of capillary walls – the valve endothelium, basement membrane, and epithelial podocytes – selectively permits certain particles to pass through while retaining others.
Yet, not all that flows into Bowman’s space becomes urine. The fluid, known as filtrate, constitutes the building blocks of what will eventually form the primary urine. It is here that the process of urine formation truly begins.
As we bid adieu to the enigmatic world of glomerular filtration, we’re left with a newfound appreciation for the artistry that resides within our very own bodies. The intricate choreography of this process remains a testament to the remarkable design of our kidneys, ceaselessly working to maintain our internal balance.
So, let us embrace the majesty of urine formation, as we raise our glasses to the intricate art of glomerular filtration. Together, we have demystified its complexities and shed light on the wonders that lie within.